Am excellent level of fitness is an essential component of success in swimming. There are many components of fitness that make up a good swimmer, the importance of each of these depends on the swimming race distance and stroke. The fitness tests used to assess a swimmer should also reflect the range of fitness components, and the interpretation of the test results should also be relative to the importance of each of these attributes. See our discussion on the fitness components for swimming.
Body Size and Shape — swimmers are usually tall and relatively lean. Some body fat is not a hindrance as it can add to buoyancy in the water. The usual anthropometric measures for swimmers would include height, weight, sitting height, arm span, hand span, body fat using skinfold measures. See more about anthropometry for swimming.
Reaction Time — the start can be very important, particularly over short distance events. The body's physical reaction time is not something that can usually be trained, though starting practice, technique and improvements in power can improve a swimmer's start.
Strength and Power — strength and power are important for a powerful explosive start off the blocks, and for quick and powerful turns. A vertical jump test is best to measure the explosive power of the legs. Upper body strength can be measured using Bench Press 1RM or 3RM tests.
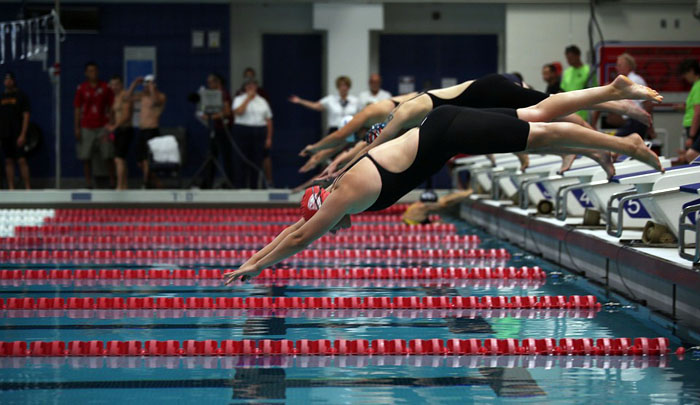 diving to start a race
diving to start a raceAnaerobic Capacity — The sprint swimming events rely heavily on the anaerobic system. The anaerobic system response to swimming can be measured by taking blood lactate measures after races and training sets. You could also look at speed drop off during a maximal 6 x 50m set with short recovery, somewhat like this anaerobic sprint fatigue test.
Endurance — aerobic capacity is important for a swimmer to maintain a high rate throughout the race, particularly the longer distance events. Land-based endurance tests (e.g. treadmill VO2max) can be used, though specific swimming tests are more relevant. A swimming VO2max test is difficult to conduct, the alternative is a swimming beep test. See our discussion and list of swimming endurance tests.
Health — lung function is obviously important for the swimmer, and checks should be made to check that the lungs are healthy and functioning to their full capacity. See lung function tests.
Swimming Specific Fitness Tests
Fitness testing for swimming usually includes training or race type test, such as 8 x 200m step test, in which heart rate, blood lactate, split times, stroke rate and perceived exertion are recorded.
Here are some other fitness tests related to swimming (see a list of fitness tests for swimmers):
- Swimming Beep Test — water based multi-stage beep test.
- Swimming VO2max Test — a progressive and maximal VO2max test conducted in a pool
- Critical Swim Speed Test — determining the theoretical swimming speed that can be maintained continuously without exhaustion.
- Swimming Step Test — a very comprehensive swimming-specific physiological test
- Shuttle swim test — a shuttle endurance swimming test like the running beep test that was designed for water polo players.
- 1 km Swim — a 1 km swim designed for testing triathletes.
- 100 m Swim Test — a swimming speed test designed for talent identification testing for triathletes.
- 500yd / 450m Swim Test — used for the Navy assessment.
- Swolf — a measure of swimming efficiency.
Related Pages
- Fitness for swimming
- Anthropometry for swimming
- List of swimming endurance tests, and list of all swimming fitness tests
- A discussion on the fitness components for swimming.
- Poll about the fitness components for swimming
- Fitness Testing for Diving and Water Polo
- The complete Fitness Test List


 Upcoming Events
Upcoming Events