Understanding and applying cycling physics principles can aid riders in optimizing their performance
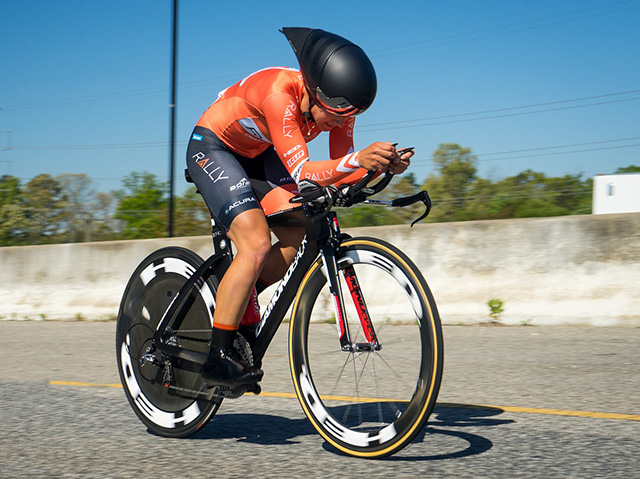 time trialling
time trialling Bike Design
There are several physics principles that are applied to bike design to enhance cycling performance. One key principle is aerodynamics, that is shaping the bike frame, handlebars, and components to reduce drag. For example, utilizing teardrop-shaped tubing reduces air resistance by allowing smoother airflow around the bike. Additionally, frame geometry adjustments, such as lowering the frontal area and incorporating aero seat posts or forks, minimize air drag, optimizing a rider's speed and efficiency.
Another physics principle applied to bike design is stiffness-to-weight ratio, which focuses on maximizing power transfer while minimizing weight. Using materials such as carbon fiber or titanium allows designers to create frames and components that are both lightweight and stiff. As well as being a lighter bike to aid in hill climbing, these features enhance the bike's responsiveness, ensuring more power from each pedal stroke, and ultimately improving acceleration and climbing capabilities.
Wheel & Tire Design
When bicycles were first invented, they had a large front wheel with a large radius. This made them extremely efficient and fast to ride on flat spaces, but unfortunately, they were quite unstable and therefore very dangerous to the rider. The center of mass was very high and the bike overturned easily.
Any cyclist will know that there are different widths of the bicycle tire depending on the terrain and intended use of the bike. Off-road bikes have wide tires and on-road racing tires have very narrow tires. Why is this so?
The thin tires are suitable for road racing bikes as they minimize friction and cut back the weight of the wheel. However, these tires are not suitable for rough surfaces - the thin tire would sink into the valleys and increase contact and friction. The fat tires are wide enough to actually float above many of the dips and troughs in the ground, as they attach only to the high spots.
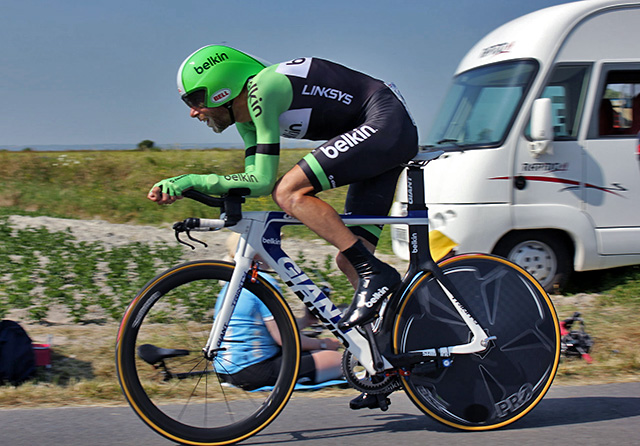 2014 Tour de France time trialling
2014 Tour de France time trialling Aerodynamics
Long-distance cycling road races are events where maximum efficiency and speed are required. The shape, body position, and equipment used can affect air resistance, impacting the rider's speed. Reducing drag through optimizing body positioning and using aerodynamic clothing and equipment can enhance performance.
Tour de France cyclist Lance Armstrong used technology to improve performance. Like all top cyclists, Lance used a specially designed helmet for time trials. The helmet design helped to shave vital seconds of his time (probably so did his drug taking!). The helmet minimizes friction by allowing air to flow over his head and down his back. An ordinary helmet would cause turbulent wind flow at his neck and create drag. He also wore specialized clothing to decrease drag.


 Upcoming Events
Upcoming Events