Sports injuries are a common occurrence among athletes of all levels, from recreational enthusiasts to professional competitors. While the physical demands of sports activities can lead to various types of injuries, understanding the underlying reasons behind these injuries is essential for prevention and proper management.
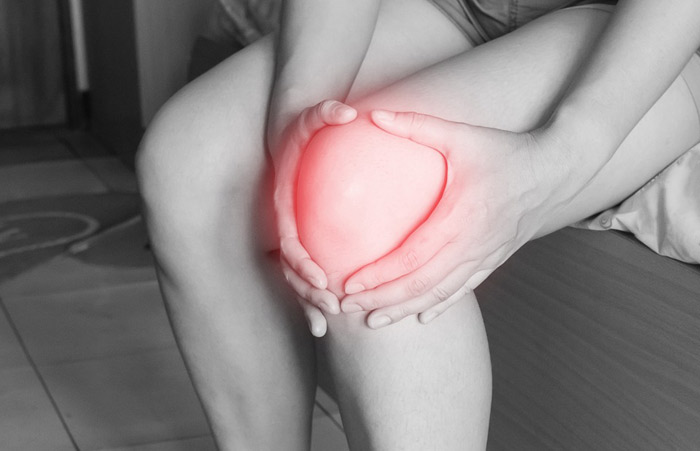 Knee Pain
Knee Pain What are some of the Common Injuries in Sports
There are quite a few different types of injuries that athletes commonly encounter. These injuries can vary in severity and may affect different parts of the body, including:
- Sprains and strains: Injuries to ligaments (sprains) and muscles or tendons (strains) often occur due to sudden movements or overstretching during activities such as basketball, where jumping and pivoting movements are common.
- Fractures: Bone fractures can result from direct trauma or repetitive stress on the bones, such as in the case of stress fractures seen in runners or gymnasts due to repetitive impact on hard surfaces.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of tendons, known as tendonitis, can occur from overuse or repetitive movements, as seen in tennis players who frequently perform overhead serves.
- Dislocations: Dislocations occur when the bones in a joint are forced out of their normal position, often due to sudden impact or twisting movements, as seen in contact sports like rugby or football.
- Concussions: Head injuries, including concussions, are common in contact sports such as football or hockey, where collisions and impacts to the head are frequent.
What are some of the Reasons for Sports Injuries
Here are some of the reasons why athletes experience sports injuries, using examples from various sports. By understanding these common reasons for sports injuries and taking proactive measures to address them, athletes can minimize their risk of injury and optimize their performance on the field, court, or track.
- Overexertion and Overtraining: Athletes who push themselves too hard or train excessively are at risk of overuse injuries. For example, a swimmer who increases their training volume too rapidly may develop shoulder tendonitis due to repetitive overhead movements.
- Poor or Inappropriate Equipment: Using improper or ill-fitting equipment can significantly increase the risk of injuries. For instance, a cyclist riding with a poorly adjusted bike saddle may develop knee pain or saddle sores due to incorrect positioning.
- Poor Nutrition or Hydration: Inadequate nutrition and hydration can impair performance and predispose athletes to injuries. Consider a long-distance runner who fails to properly hydrate during a marathon, leading to dehydration and muscle cramps that hinder performance and increase the risk of injury.
- Ignoring Pain or Injury: Athletes who ignore warning signs such as pain or discomfort are more likely to exacerbate existing injuries or develop new ones. For example, a soccer player who continues to play despite experiencing persistent ankle pain may aggravate an existing sprain, leading to further ligament damage and prolonged recovery time.
- Lack of Proper Warm-up and Stretching: Skipping warm-up exercises and neglecting to stretch before engaging in physical activity can leave muscles susceptible to strains and tears. Take, for instance, a basketball player who fails to properly warm up before a game and subsequently suffers a hamstring strain while sprinting down the court due to tight muscles.
Related Pages
- Injury treatment in sports
- Sports Medicine
Disclaimer


 Current Events
Current Events